Product Detail
Product NameKCTD16 Antibody
Host SpeciesRabbit
ClonalityPolyclonal
PurificationAntigen affinity purification.
ApplicationsWB IHC
Species ReactivityHu Ms
SpecificityThe antibody detects endogenous levels of total KCTD16 protein.
Immunogen Typeprotein
Immunogen DescFusion protein of human KCTD16
Target NameKCTD16
ConjugateUnconjugated
Other NamesBTB/POZ domain-containing protein KCTD16; DKFZp781A1155; KCD16; KCTD16; KIAA1317; MGC138167
Accession NoSwiss-Prot#: Q68DU8
Gene ID: 57528
Uniprot
Q68DU8
Gene ID
57528;
Calculated MW49kd
Concentration1.6mg/ml
FormulationRabbit IgG in pH7.4 PBS, 0.05% NaN3, 40% Glycerol.
StorageStore at -20˚C
Application Details
Western blotting: 1:500-1:2000
Immunohistochemistry: 1:25-1:100
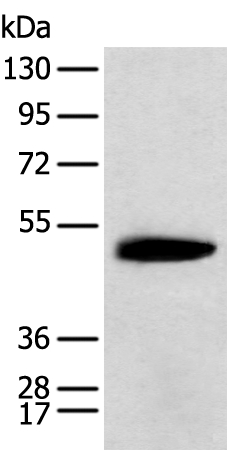
Gel: 8%SDS-PAGE
Lysate: 40 μg
Lane: Mouse brain tissue
Primary antibody: 1/400 dilution
Secondary antibody: Goat anti rabbit IgG at 1/8000 dilution
Exposure time: 3 seconds
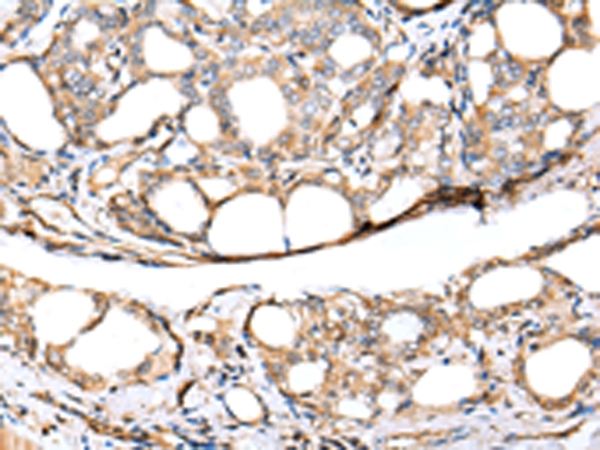
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded Human colorectal cancer tissue using #42919 at dilution 1/30.
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded Human thyroid cancer tissue using #42919 at dilution 1/30.
The BTB (Broad-Complex, Tramtrack and Bric a brac) domain, also known as the POZ (Poxvirus and Zinc finger) domain, is an N-terminal homodimerization domain that contains multiple copies of kelch repeats and/or C2H2-type zinc fingers. Proteins that contain BTB domains are thought to be involved in transcriptional regulation via control of chromatin structure and function. KCTD16 (potassium channel tetramerisation domain containing 16), also known as BTB/POZ domain-containing protein KCTD16, is a 428 amino acid protein that contains one BTB (POZ) domain. An auxiliary subunit of GABAB R1 and GABAB R2, KCTD16 increases agonist potency and alters the G-protein signaling of the receptors by accelerating onset and promoting desensitization.
If you have published an article using product 42919, please notify us so that we can cite your literature.
et al,Identification and study of mood-related biomarkers and potential molecular mechanisms in type 2 diabetes mellitus.
, (2025),
PMID:
39915429



 The lead time is currently 1 week.
The lead time is currently 1 week.