Product Detail
Product NameABCG1 Rabbit mAb
Clone No.SU03-26
Host SpeciesRecombinant Rabbit
Clonality Monoclonal
PurificationProA affinity purified
ApplicationsWB, ICC/IF, IHC
Species ReactivityHu, Rt
Immunogen Descrecombinant protein
ConjugateUnconjugated
Other NamesABC transporter 8 antibody ABC8 antibody ABCG1 antibody ABCG1_HUMAN antibody ATP-binding cassette sub family G member 1 antibody ATP-binding cassette sub-family G member 1 antibody ATP-binding cassette transporter 8 antibody ATP-binding cassette transporter member 1 of subfamily G antibody ATP-binding cassette, sub family G WHITE member 1 antibody homolog of Drosophila white antibody MGC34313 antibody White protein homolog antibody White protein homolog ATP binding cassette transporter 8 antibody WHITE1 antibody WHT1 antibody
Accession NoSwiss-Prot#:P45844
Uniprot
P45844
Gene ID
9619;
Calculated MW110 kDa
Formulation1*TBS (pH7.4), 1%BSA, 40%Glycerol. Preservative: 0.05% Sodium Azide.
StorageStore at -20˚C
Application Details
WB: 1:1,000-1:2,000
IHC: 1:50-1:200
ICC: 1:50-1:200
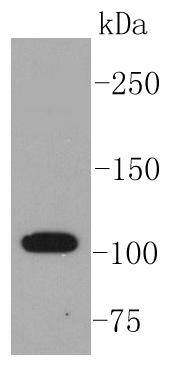
Western blot analysis of ABCG1 on THP-1 cell lysates using anti-ABCG1 antibody at 1/1,000 dilution.
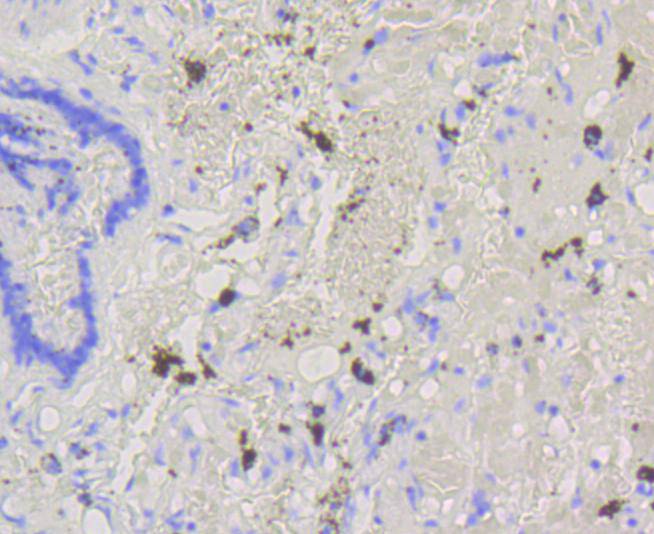
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human lung tissue using anti-ABCG1 antibody. Counter stained with hematoxylin.
ABCG1 (also designated ABC8 or human white gene), a member of the evolutionary conserved family of ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters, exhibits high homology with the Drosophila white gene. ABC transporters couple the energy of ATP hydrolysis to the translocation of various molecules across biological membranes. These proteins contain characteristic ATP-binding domains and transmembrane domains which form a channel-like structure for transport. ABCG1 functions to regulate cholesterol and phospholipid transport in macrophages. ABCG1 is highly expressed in several tissues, including brain, spleen, lung and placenta, and has been localized to the cell surface and intracellular compartments of cholesterol-laden macrophages.
If you have published an article using product 48812, please notify us so that we can cite your literature.
et al,Niacin-induced lysosomal free cholesterol efflux via LXRα-mediated signaling pathways in macrophages retards the progression of atherosclerosis
, (2025),
PMID:


 Yes
Yes