Lysine lactylation is a significant, newly discovered post-translational modification (PTM) with major implications in cancer biology.
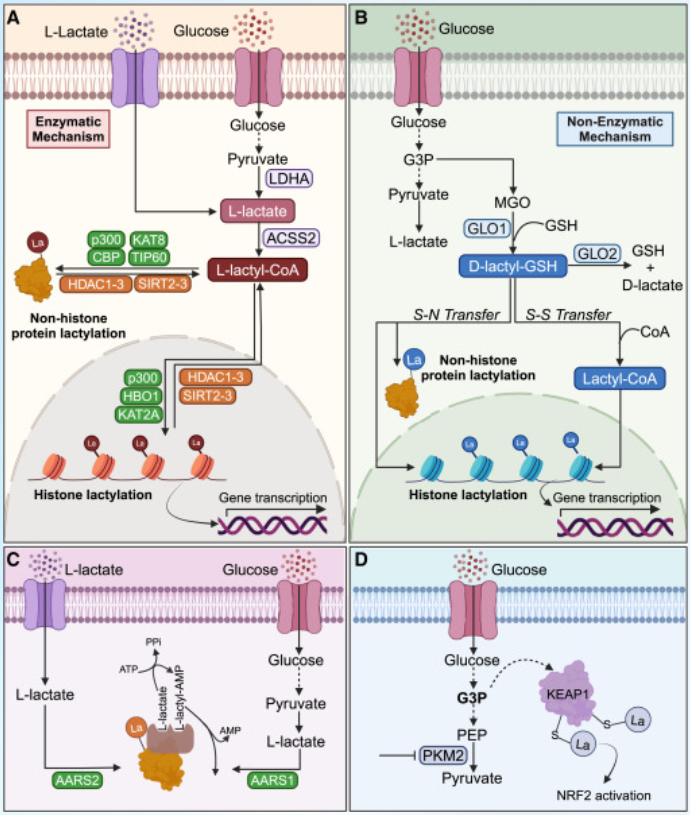



L-lactyl-CoA (precursor of the L-lactyl moiety) and S-D-lactylglutathione (precursor of the D-lactyl moiety), which enable enzymatic and non-enzymatic mechanisms of lysine lactylation, respectively. Initially found on histone proteins (e.g., H3K9, H3K18, H3K56, H4K8, H4K12), it is now known to also modify non-histone proteins like metabolic enzymes and transcription factors.

It plays a pivotal role in transcriptional activation and regulates protein function, stability, and cellular interactions.

The modification can be added via an enzymatic pathway (using L-lactyl-CoA) or a non-enzymatic pathway (using S-D-lactylglutathione). While specific regulatory enzymes are unknown, existing acetyltransferases and deacetylases are likely involved.

Lysine lactylation influences critical pathways in malignant transformation and metastasis, making it a promising new target for cancer therapy.
 |
|||
Cat No |
Name |
Species Reactivity |
Applications |
HL001 |
Species independent |
WB,IHC,IP,IF,FC,ChIP |
|
HL002 |
Species independent |
WB;IF;ChIP |
|
HL003 |
Human;Mouse;Rat |
WB;IHC;IF;IP |
|
HL004 |
Human;Mouse;Rat |
WB |
|
HL005 |
Human;Mouse;Rat |
WB;IHC;IF;ChIP |
|
HL006 |
Human |
WB |
|
HL007 |
Human;Mouse;Rat |
WB;IHC;ChIP |
|
HL008 |
Human;Mouse;Rat |
WB;IHC;IP |
|
HL009 |
Human;Mouse;Rat |
WB;IHC;IF;ChIP |
|
HL011 |
Human;Mouse;Rat |
WB;IF;IP |
|
HL012 |
Human;Mouse;Rat |
WB;IP |
|
HL013 |
Human;Mouse;Rat |
WB;IP |
|
HL014 |
Human;Mouse |
WB;IP |
|
HL015 |
Human;Mouse |
WB;IP |
|
HL016 |
|||


 |
|||
Cat No |
Name |
Species Reactivity |
Applications |
12828 |
Species independent |
WB,IHC,IF |
|
12829 |
Species independent |
WB,IHC |
|
HW225 |
Human,Mouse,Rat |
WB, ICC/IF, IHC |
|
49065 |
Human,Mouse,Rat |
WB, ICC/IF, IHC |
|
HW010 |
Human,Mouse,Rat |
WB,IHC,IF |
|
HW036 |
Human,Mouse,Rat |
WB,IHC,IF |
|
HW027 |
Human,Mouse,Rat |
WB,IHC,IF |
|
