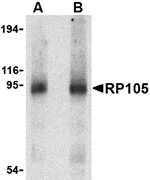
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are evolutionarily conserved pattern-recognition molecules resembling the toll proteins that mediate antimicrobial responses in Drosophila. These proteins recognize different microbial products during infection and serve as an important link between the innate and adaptive immune responses. The signaling of these TLRs is kept under tight control by the expression of endogenous inhibiting proteins. One such protein is RP105, a recently identified homolog to TLR4 that, with MD-1, interacts with and inhibits the TLR4/MD-2 signaling pathway. It has also been suggested that the RP105/MD-1 complex influences antibody production mediated by both TLR4/MD-2 and TLR2 receptor complexes.