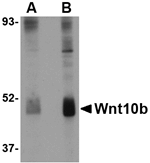
Wnt10b is a member of the Wnt family, a gene family that encodes secreted signaling proteins that play crucial roles in normal development such as regulation of cell fate and patterning during embryogenesis as well as neoplastic transformation. Wnt10b is found in the mouse mammary tumor virus insertion site where it is activated and causes mammary tumors. Elevated levels of Wnt10b have also been detected in human breast carcinomas. Wnt10b is known to be involved in adipogenesis, maintaining the preadipocyte in an undifferentiated state. More recently, Wnt10b has been shown to promote epithelial cell differentiation and hair shaft growth, demonstrating that Wnt10b has multiple roles in cell growth and differentiation.