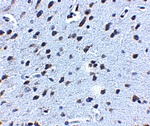
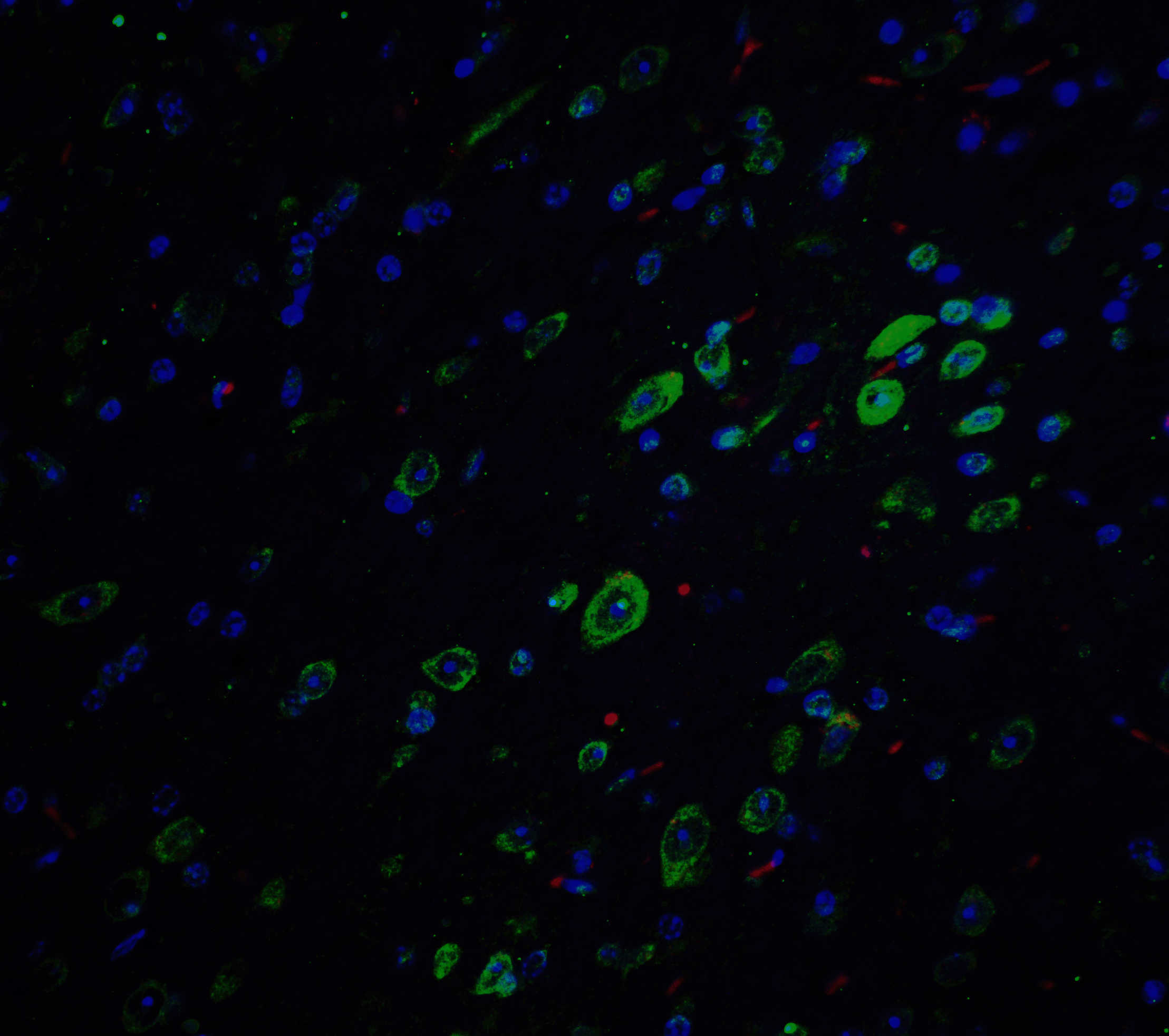
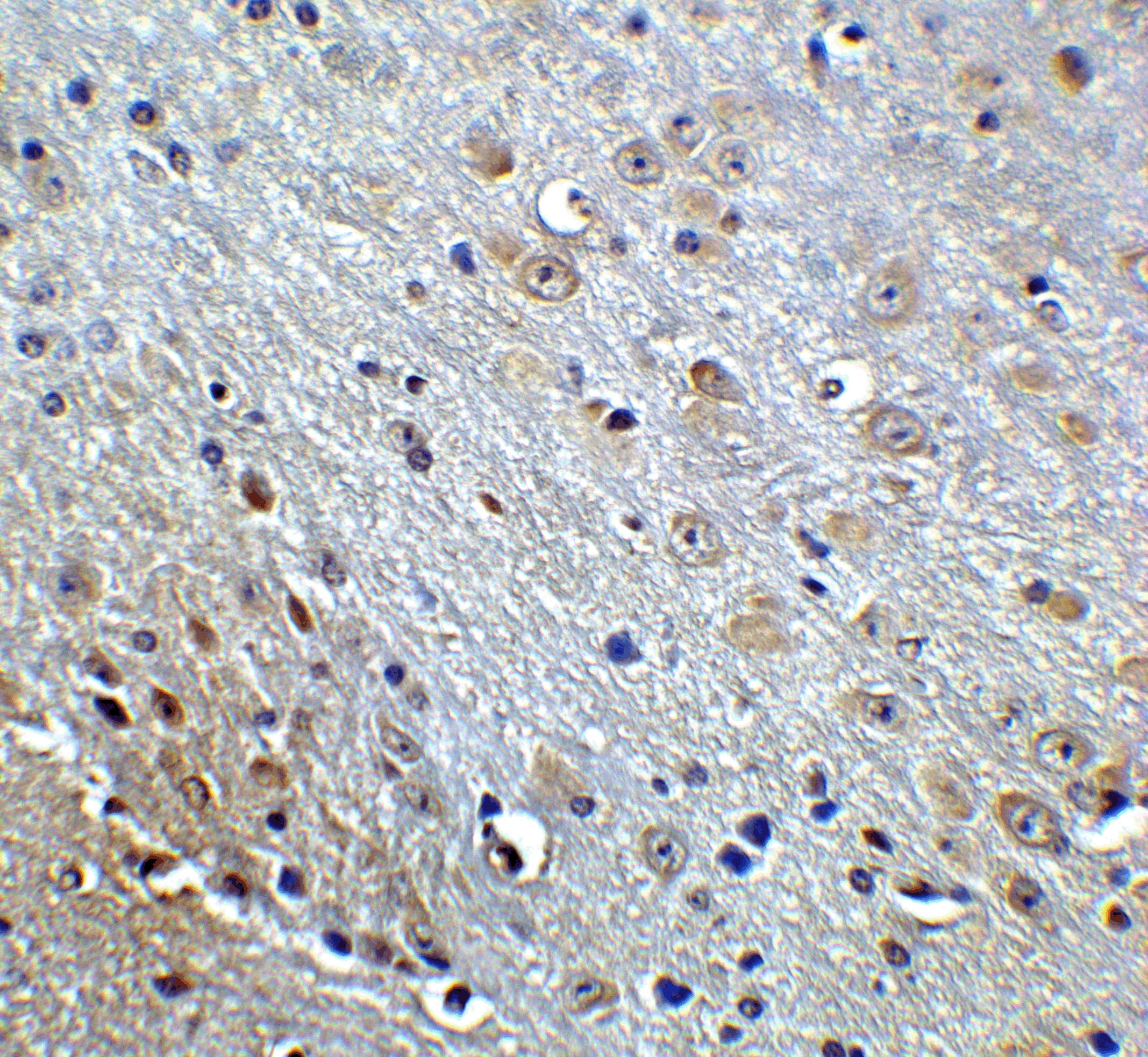
Accumulation of the amyloid-beta peptide (Abeta) in the cerebral cortex is a critical event in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. The beta?amyloid protein precursor (APP) is cleaved by one of two beta?secretases (BACE and BACE2), producing a soluble derivative of the protein and a membrane anchored 99-amino acid carboxy-terminal fragment (C99). The C99 fragment serves as substrate for gamma?secretase to generate the 4 kDa amyloid-beta peptide (Abeta), which is deposited in the Alzheimer’s disease patients’ brains. Recently, Death Receptor 6 (DR6) was found to interact with an amino-terminal fragment of the Beta-amyloid protein (N-APP) in neurons, activating a caspase 6-dependent apoptotic event leading to axonal degeneration and pruning during development, suggesting that these two proteins are involved in neural development and may possibly play a role in Alzheimer’s disease.