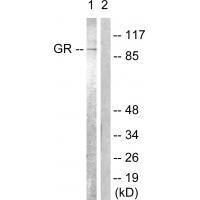
Receptor for glucocorticoids (GC). Has a dual mode of action: as a transcription factor that binds to glucocorticoid response elements (GRE), both for nuclear and mitochondrial DNA, and as a modulator of other transcription factors. Affects inflammatory responses, cellular proliferation and differentiation in target tissues. Could act as a coactivator for STAT5-dependent transcription upon growth hormone (GH) stimulation and could reveal an essential role of hepatic GR in the control of body growth. Involved in chromatin remodeling. May play a negative role in adipogenesis through the regulation of lipolytic and antilipogenic genes expression.
Kyung Jin Kwak, J. Exp. Bot., Nov 2005; 56: 3007 - 3016.
Maite de Llanos, Hum. Reprod., Jan 2005; 20: 216 - 220.
M. Lynch, Mol. Hum. Reprod., Jul 2005; 11: 507 - 512.
Valeriya P. Makarenkova, J. Immunol., Feb 2006; 176: 2085 - 2094.