Product Detail
Product NameNFkB-p65(Ab-276) Antibody
Host SpeciesRabbit
ClonalityPolyclonal
PurificationAntibodies were produced by immunizing rabbits with synthetic peptide and KLH conjugates. Antibodies were purified by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific peptide.
ApplicationsWB IHC IF
Species ReactivityHu Ms Rt
SpecificityThe antibody detects endogenous level of total NFkB-p65 protein.
Immunogen TypePeptide-KLH
Immunogen DescPeptide sequence around aa.274~278 (R-P-S-D-R) derived from Human NFkB-p65.
Target NameNFkB-p65
ConjugateUnconjugated
Other NamesNFKB3; RELA; TF65; Transcription factor p65; p65
Accession NoSwiss-Prot: Q04206
NCBI Protein: NP_001138610.1
Uniprot
Q04206
Gene ID
5970;
Concentration1.0mg/ml
FormulationSupplied at 1.0mg/mL in phosphate buffered saline (without Mg2+ and Ca2+), pH 7.4, 150mM NaCl, 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol.
StorageStore at -20°C for long term preservation (recommended). Store at 4°C for short term use.
Application Details
Predicted MW: 65kd
Western blotting: 1:500~1:1000
Immunohistochemistry: 1:50~1:100
Immunofluorescence: 1:100~1:200
Western blot analysis of extracts from Hela cells using NFkB-p65(Ab-276) Antibody #21011 and the same antibody preincubated with blocking peptide.
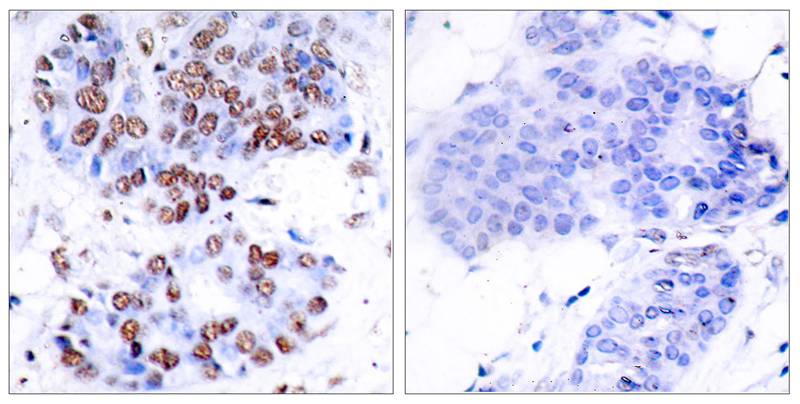
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human breast carcinoma tissue using NFkB-p65(Ab-276) Antibody #21011(left) or the same antibody preincubated with blocking peptide(right).
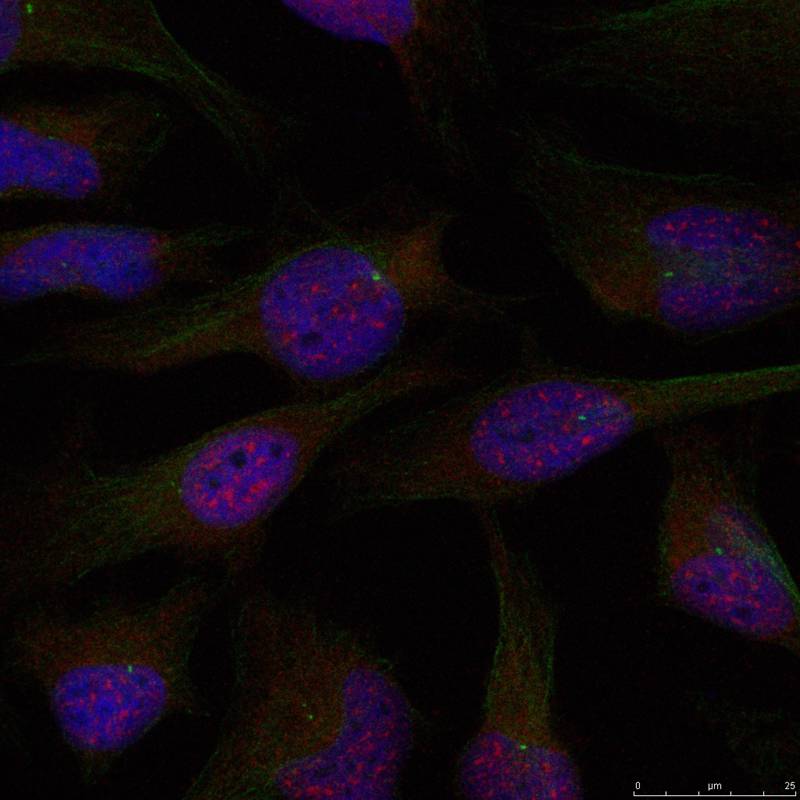
Immunofluorescence staining of methanol-fixed Hela cells using NFkB-p65(Ab-276) Antibody #21011.
NF-kappa-B is a pleiotropic transcription factor which is present in almost all cell types and is involved in many biological processed such as inflammation, immunity, differentiation, cell growth, tumorigenesis and apoptosis. NF-kappa-B is a homo- or heterodimeric complex formed by the Rel-like domain-containing proteins RELA/p65, RELB, NFKB1/p105, NFKB1/p50, REL and NFKB2/p52 and the heterodimeric p65-p50 complex appears to be most abundant one. The dimers bind at kappa-B sites in the DNA of their target genes and the individual dimers have distinct preferences for different kappa-B sites that they can bind with distinguishable affinity and specificity. Different dimer combinations act as transcriptional activators or repressors, respectively. NF-kappa-B is controlled by various mechanisms of post-translational modification and subcellular compartmentalization as well as by interactions with other cofactors or corepressors. NF-kappa-B complexes are held in the cytoplasm in an inactive state complexed with members of the NF-kappa-B inhibitor (I-kappa-B) family. In a conventional activation pathway, I-kappa-B is phosphorylated by I-kappa-B kinases (IKKs) in response to different activators, subsequently degraded thus liberating the active NF-kappa-B complex which translocates to the nucleus. NF-kappa-B heterodimeric p65-p50 and p65-c-Rel complexes are transcriptional activators. The NF-kappa-B p65-p65 complex appears to be involved in invasin-mediated activation of IL-8 expression. The inhibitory effect of I-kappa-B upon NF-kappa-B the cytoplasm is exerted primarily through the interaction with p65. p65 shows a weak DNA-binding site which could contribute directly to DNA binding in the NF-kappa-B complex
Baeuerle P A, et al. (1994) Annu Rev Immunol. 12:141-179.
Baeuerle P A, et al. (1996) Cell 87:13-20.
Haskill S, et al. (1991) Cell 65:1281-1289.
Thompson J E, et al. (1995) Cell 80: 573-582.
If you have published an article using product 21011, please notify us so that we can cite your literature.
et al,Platelet-Rich Plasma Releasate Inhibits Inflammatory Processes in Osteoarthritic Chondrocytes.
, (2011),
PMID:
21856929
et al,Peroxisome proliferator activated receptor alpha activation decreases inflammatory and destructive responses in osteoarthritic cartilage.
, (2011),
PMID:
21458577
et al,Platelet-rich plasma releasate inhibits inflammatory processes in osteoarthritic chondrocytes. In Am J Sports Med on 2011 Nov by Gerben M van Buul, Wendy L M Koevoet, et al..PMID: 21856929
, (2011),
PMID:
21856929
et al,Tiagabine protects dopaminergic neurons against neurotoxins by inhibiting microglial activation.In Sci Rep on 2015 Oct 26 by Jie Liu , Dongping Huang et al..PMID: 26499517
, (2015),
PMID:
26499517



 Yes
Yes