Product Detail
Product NameORAI3 Monoclonal Antibody
Clone No.mAb (Clone 2H2G9)
Host SpeciesMouse
ClonalityMonoclonal
PurificationImmunoaffinity chromotography purified IgG
ApplicationsELISA WB IHC
Species ReactivityHu Rt
Immunogen TypePeptide
Immunogen DescA 19 amino acid peptide from near the carboxy terminus of human ORAI3.
Target NameORAI3
ConjugateUnconjugated
Other NamesORAI3 (2H2G9), Transmembrane protein 142C, TMEM142C, Calcium release-activated calcium channel protein 3
Accession NoSwiss-Prot:Q9BRQ5
Gene ID:93129
Uniprot
Q9BRQ5
Gene ID
93129;
Concentration1mg/ml
FormulationSupplied in PBS containing 0.02% sodium azide.
StorageCan be stored at -20˚C, stable for one year.
Application Details
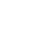
Western blot analysis of ORAI3 in rat spleen lysate with ORAI3 antibody at 2 ug/mL.
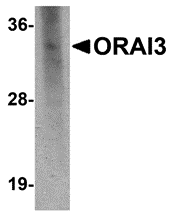
Immunohistochemistry of ORAI3 in rat spleen tissue with ORAI3 antibody at 2.5 ug/mL.
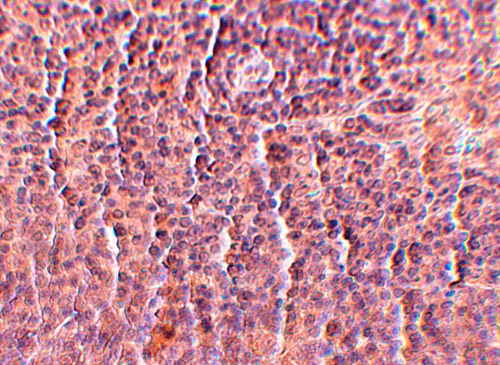
Immunofluorescence of ORAI3 in human spleen tissue with ORAI3 antibody at 5 μg/ml.
Antigen stimulation of immune cells triggers Ca++ entry t hrough Ca++ release-activated Ca++ (CRAC) channels. ORAI3 is one of two mammalian homologs to ORAI1, a recently identified four-transmembrane spanning protein that is an essential component of CRAC. All three homologs have been shown to function as Ca++ plasma membrane channels gated through interactions with STIM1, the store-activated endoplasmic reticulum Ca++ sensor. However, ORAI3 channels failed to produce detectable Ca++ selective currents in cells co-transfected with ORAI3 and STIM1, indicating that ORAI3 channels undergo a lesser degree of depotentiation than ORAI1 or ORAI2. Na+ currents through ORAI1, 2 and 3 channels were equally inhibited by extracellular Ca++, indicating that each have similar affinities for Ca++ within the selectivity filter. This antibody is predicted to have no cross-reactivity to ORAI1 or ORAI2. Larger molecular weight bands are sometimes seen in SDS-PAGE; these may represent post-translationally modified ORAI 3.
If you have published an article using product 26028, please notify us so that we can cite your literature.


 Yes
Yes