Product Detail
Product NameChk2 Rabbit mAb
Clone No.SC604
Host SpeciesRecombinant Rabbit
Clonality Monoclonal
PurificationProA affinity purified
ApplicationsWB, ICC/IF, IHC, IP
Species ReactivityHu
Immunogen Descrecombinant protein
ConjugateUnconjugated
Other NamesCDS 1 antibody Cds1 antibody Cds1 homolog antibody Checkpoint kinase 2 antibody Checkpoint like protein CHK2 antibody CHEK 2 antibody Chek2 antibody Chk 2 antibody CHK2 checkpoint homolog (S. pombe) antibody CHK2 checkpoint homolog antibody CHK2_HUMAN antibody hCds1 antibody HuCds 1 antibody LFS 2 antibody LFS2 antibody PP1425 antibody RAD 53 antibody RAD53 antibody Rad53 homolog antibody Serine/threonine protein kinase Chk2 antibody Serine/threonine-protein kinase Chk2 antibody
Accession NoSwiss-Prot#:O96017
Uniprot
O96017
Gene ID
11200;
Calculated MW62 kDa
Formulation1*TBS (pH7.4), 1%BSA, 40%Glycerol. Preservative: 0.05% Sodium Azide.
StorageStore at -20˚C
Application Details
WB: 1:1,000-1:2,000
IHC: 1:50-1:200
ICC: 1:50-1:200
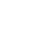
Western blot analysis of Chk2 on Hela cells lysates using anti-Chk2 antibody at 1/1,000 dilution.
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human spleen tissue using anti-Chk2 antibody. Counter stained with hematoxylin.
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human breast carcinoma tissue using anti-Chk2 antibody. Counter stained with hematoxylin.
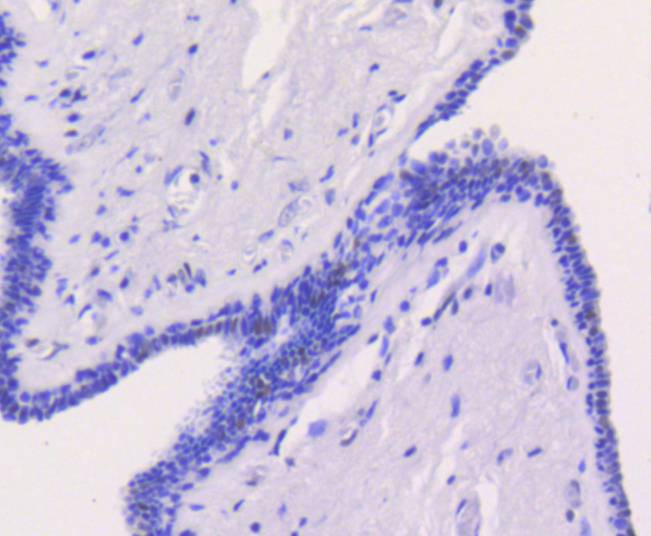
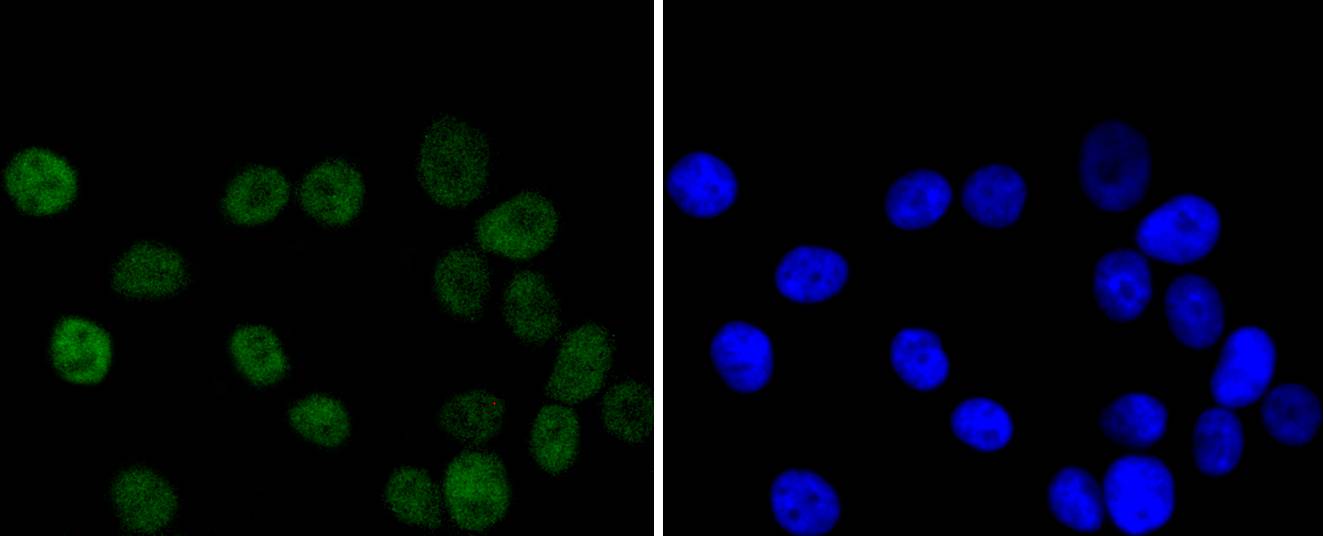
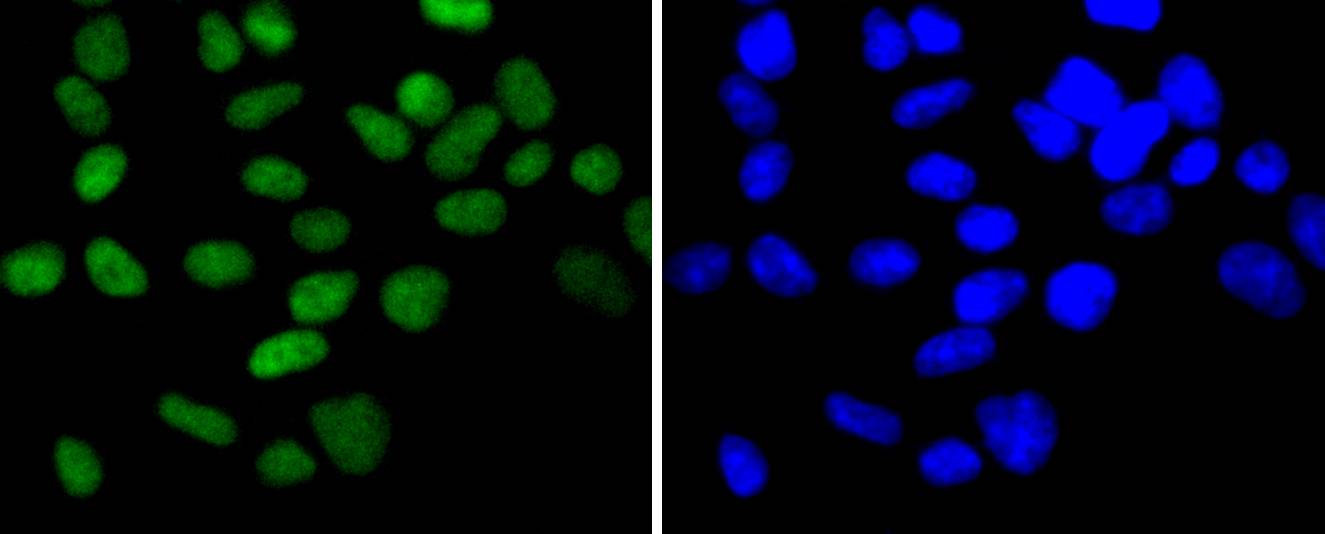
ICC staining Chk2 in Hela cells (green). The nuclear counter stain is DAPI (blue). Cells were fixed in paraformaldehyde, permeabilised with 0.25% Triton X100/PBS.
ICC staining Chk2 in MCF-7 cells (green). The nuclear counter stain is DAPI (blue). Cells were fixed in paraformaldehyde, permeabilised with 0.25% Triton X100/PBS.
ICC staining Chk2 in 293 cells (green). The nuclear counter stain is DAPI (blue). Cells were fixed in paraformaldehyde, permeabilised with 0.25% Triton X100/PBS.
Cell cycle events are regulated by the sequential activation and deactivation of cyclin dependent kinases (Cdks) and by proteolysis of cyclins. Chk1 and Chk2 are involved in these processes as regulators of Cdks. Chk1 and Chk2 both function as essential components in the G2 DNA damage checkpoint by phosphorylating Cdc25C in response to DNA damage. Phosphorylation inhibits Cdc25C activity, thereby blocking mitosis. Cdc25A, Cdc25B and Cdc25C protein tyrosine phosphatases function as mitotic activators by dephosphorylating Cdc2 p34 on regulatory tyrosine residues. It has also been shown that Chk1 can phosphorylate Wee1 in vitro, providing evidence that the hyperphosphorylated form of Wee1, seen in cells delayed by Chk1 overexpression, is due to phosphorylation by Chk1.
If you have published an article using product 48967, please notify us so that we can cite your literature.



 Yes
Yes