Product Detail
Product NameFerritin Rabbit mAb
Clone No.SC0620
Host SpeciesRecombinant Rabbit
Clonality Monoclonal
PurificationProA affinity purified
ApplicationsWB, ICC/IF
Species ReactivityHu, Ms, Rt, zebrafish
Immunogen Descrecombinant protein
ConjugateUnconjugated
Other NamesCell proliferation-inducing gene 15 protein antibody
Ferritin H subunit antibody
Ferritin heavy chain antibody
Ferritin heavy polypeptide 1 antibody
Ferritin L subunit antibody
Ferritin light polypeptide antibody
Ferritin, heavy polypeptide antibody
FRIH_HUMAN antibody
FTH antibody
FTH1 antibody
FTL antibody
Accession NoSwiss-Prot#:P02792
Uniprot
P02792
Gene ID
2512;
Calculated MW21 kDa
Formulation1*TBS (pH7.4), 1%BSA, 40%Glycerol. Preservative: 0.05% Sodium Azide.
StorageStore at -20˚C
Application Details
WB: 1:500-1:1,000
ICC: 1:50-1:200
Western blot analysis of Ferritin on zebrafish lysates using anti-Ferritin antibody at 1/1,000 dilution.
Western blot analysis of Ferritin on hybrid fish (crucian-carp) liver tissue lysate using anti-Ferritin antibody at 1/500 dilution.
ICC staining Ferritin in SHG-44 cells (green). The nuclear counter stain is DAPI (blue). Cells were fixed in paraformaldehyde, permeabilised with 0.25% Triton X100/PBS.
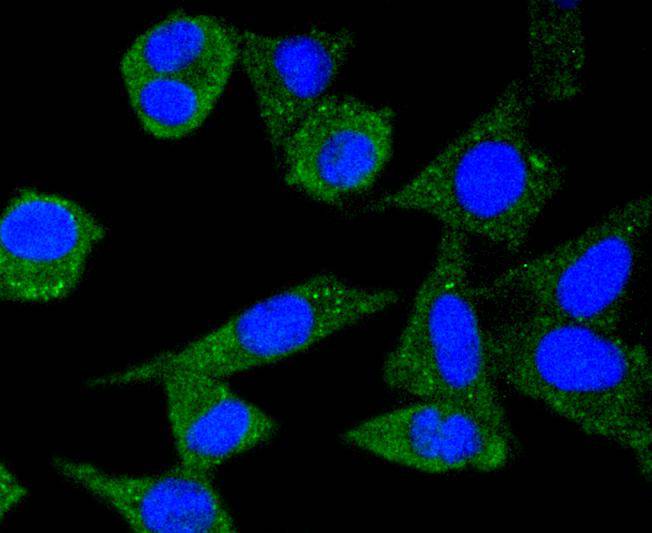
ICC staining Ferritin in MCF-7 cells (green). The nuclear counter stain is DAPI (blue). Cells were fixed in paraformaldehyde, permeabilised with 0.25% Triton X100/PBS.
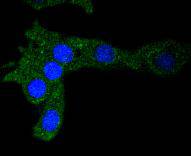
ICC staining Ferritin in SH-SY-5Y cells (green). The nuclear counter stain is DAPI (blue). Cells were fixed in paraformaldehyde, permeabilised with 0.25% Triton X100/PBS.
Mammalian ferritins consist of 24 subunits made up of two types of polypeptide chains, ferritin heavy chain and ferritin light chain, which each have unique functions. Ferritin heavy chains catalyze the first step in iron storage, the oxidation of Fe (II), whereas ferritin light chains promote the nucleation of ferrihydrite, enabling storage of Fe (III). The most prominent role of mammalian ferritins is to provide iron-buffering capacity to cells. In addition to iron buffering, heavy chain ferritin is also involved in the regulation of thymidine biosynthesis via increased expression of cytoplasmic serine hydroxymethyltransferase, which is a limiting factor in thymidylate synthesis in MCF-7 cells. Light chain ferritin is involved in cataracts by at least two mechanisms, hereditary hyperferritinemia cataract syndrome, in which light chain ferritin is overexpressed, and oxidative stress, an important factor in the development of ageing-related cataracts. The gene encoding human ferritin heavy chain maps to chromosome 11q13 and the human ferritin light chain gene maps to chromosome 19q13.3-q13.4.
If you have published an article using product 48995, please notify us so that we can cite your literature.





 Yes
Yes