Product Detail
Product NameHistone H1.0 Rabbit mAb
Clone No.SD206-04
Host SpeciesRecombinant Rabbit
Clonality Monoclonal
PurificationProA affinity purified
ApplicationsWB, ICC/IF, IHC
Species ReactivityHu, Ms, Rt
Immunogen Descrecombinant protein
ConjugateUnconjugated
Other NamesH1 histone family member 0 antibody H1(0) antibody H10 antibody H10_HUMAN antibody h1f0 antibody H1FV antibody Histone H1'' antibody Histone H1(0) antibody Histone H1.0 antibody Histone H10 antibody Histone H5 antibody MGC5241 antibody N-terminally processed antibody
Accession NoSwiss-Prot#:P07305
Uniprot
P07305
Gene ID
3005;
Calculated MW28 kDa
Formulation1*TBS (pH7.4), 1%BSA, 40%Glycerol. Preservative: 0.05% Sodium Azide.
StorageStore at -20˚C
Application Details
WB: 1:1,000-5,000
IHC: 1:50-1:200
ICC: 1:50-1:200
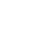
Western blot analysis of Histone H1.0 on human lung lysates using anti-Histone H1.0 antibody at 1/1,000 dilution.
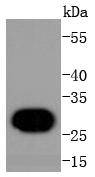
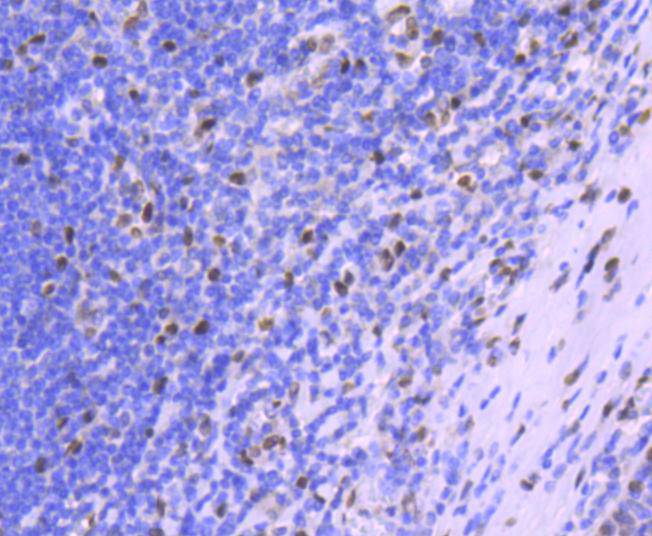
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human tonsil tissue using anti-Histone H1.0 antibody. Counter stained with hematoxylin.
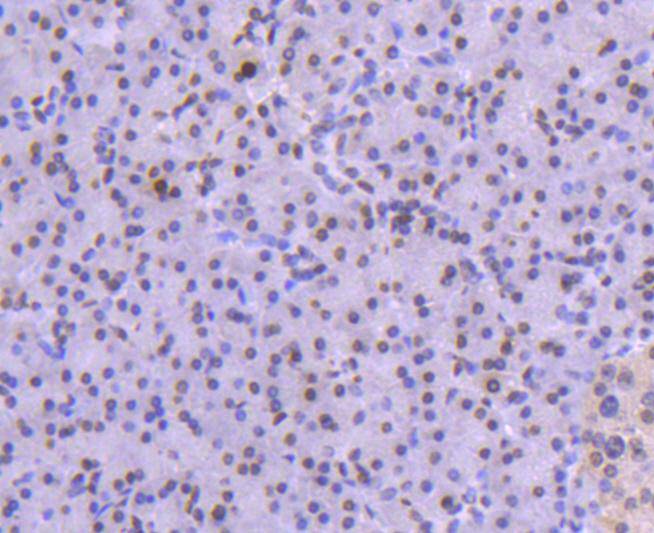
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human breast carcinoma tissue using anti-Histone H1.0 antibody. Counter stained with hematoxylin.
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human pancreas tissue using anti-Histone H1.0 antibody. Counter stained with hematoxylin.
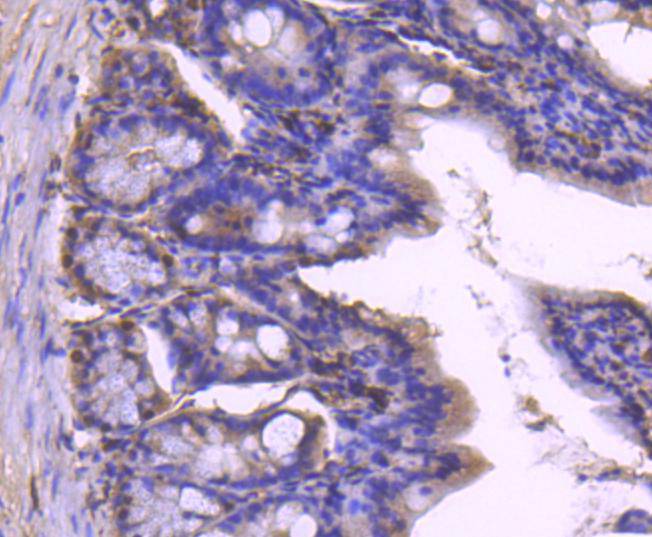
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded mouse colon tissue using anti-Histone H1.0 antibody. Counter stained with hematoxylin.
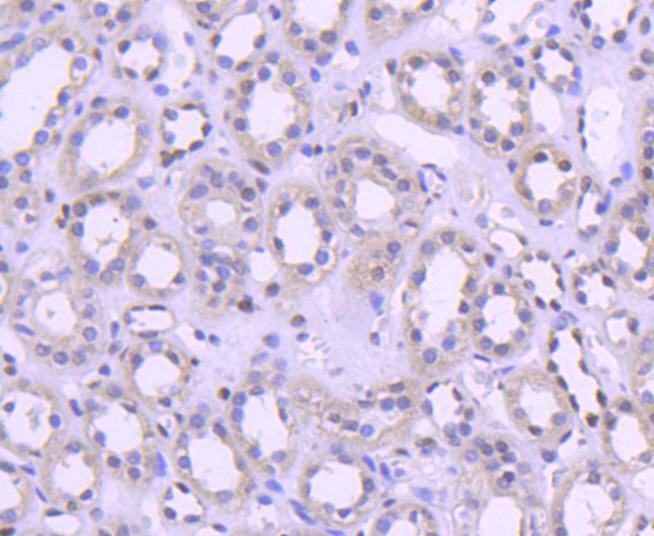
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human kidney tissue using anti-Histone H1.0 antibody. Counter stained with hematoxylin.
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded mouse liver tissue using anti-Histone H1.0 antibody. Counter stained with hematoxylin.
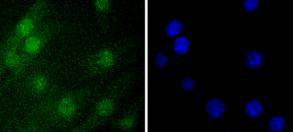
ICC staining Histone H1.0 in NIH/3T3 cells (green). The nuclear counter stain is DAPI (blue). Cells were fixed in paraformaldehyde, permeabilised with 0.25% Triton X100/PBS.
Eukaryotic histones are basic and water soluble nuclear proteins that form hetero-octameric nucleosome particles by wrapping 146 base pairs of DNA in a left-handed super-helical turn sequentially to form chromosomal fiber. Two molecules of each of the four core histones (H2A, H2B, H3, and H4) form the octamer; formed of two H2A-H2B dimers and two H3-H4 dimers, forming two nearly symmetrical halves by tertiary structure. Over 80% of nucleosomes contain the linker Histone H1, derived from an intronless gene, that interacts with linker DNA between nucleosomes and mediates compaction into higher order chromatin. Histones are subject to posttranslational modification by enzymes primarily on their N-terminal tails, but also in their globular domains. Such modifications include methylation, citrullination, acetylation, phosphorylation, sumoylation, ubiquitination and ADP-ribosylation.
If you have published an article using product 49133, please notify us so that we can cite your literature.



 Yes
Yes