Product Detail
Product NameHDAC8 Rabbit mAb
Clone No.SD082-07
Host SpeciesRecombinant Rabbit
Clonality Monoclonal
PurificationProA affinity purified
ApplicationsWB, IP, FC
Species ReactivityHu, Ms, Rt
Immunogen Descrecombinant protein
ConjugateUnconjugated
Other NamesCDA07 antibody CDLS5 antibody HD 8 antibody HD8 antibody HDAC 8 antibody Hdac8 antibody HDAC8_HUMAN antibody HDACL 1 antibody HDACL1 antibody Histone deacetylase 8 antibody Histone deacetylase like 1 antibody MRXS6 antibody RPD 3 antibody RPD3 antibody WTS antibody
Accession NoSwiss-Prot#:Q9BY41
Uniprot
Q9BY41
Gene ID
55869;
Calculated MW42 kDa
Formulation1*TBS (pH7.4), 1%BSA, 40%Glycerol. Preservative: 0.05% Sodium Azide.
StorageStore at -20˚C
Application Details
WB: 1:1,000-1:2,000
FC: 1:50-1:100
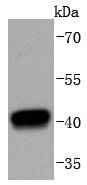
Western blot analysis of HDAC8 on K562 cells lysates using anti-HDAC8 antibody at 1/1,000 dilution.
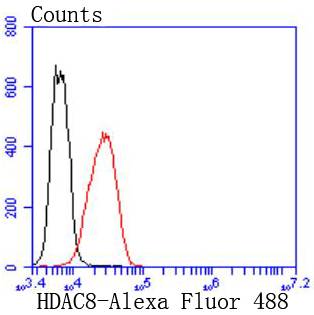
Flow cytometric analysis of K562 cells with HDAC8 antibody at 1/50 dilution (red) compared with an unlabelled control (cells without incubation with primary antibody; black). Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated goat anti rabbit IgG was used as the secondary antibody
In the intact cell, DNA closely associates with histones and other nuclear proteins to form chromatin. The remodeling of chromatin is believed to be a critical component of transcriptional regulation and a major source of this remodeling is brought about by the acetylation of nucleosomal histones. Acetylation of lysine residues in the amino terminal tail domain of histone results in an allosteric change in the nucleosomal conformation and an increased accessibility to transcription factors by DNA. Conversely, the deacetylation of histones is associated with transcriptional silencing. Several mammalian proteins have been identified as nuclear histone acetylases, including GCN5, PCAF (p300/CBP-associated factor), p300/CBP, HAT1 and the TFIID subunit TAF II p250. Mammalian HDAC8, isolated from human kidney, is a histone deacetylase that shares homology to other HDACs but has different tissue distribution. HDAC8 is localized to the nucleus and plays a role in the development of a broad range of tissues and in the etiology of cancer.
If you have published an article using product 49206, please notify us so that we can cite your literature.


 Yes
Yes