Product Detail
Product NameTissue-type plasminogen activator Rabbit mAb
Clone No.JF0958
Host SpeciesRecombinant Rabbit
Clonality Monoclonal
PurificationProA affinity purified
ApplicationsWB, IHC
Species ReactivityHu, Ms, Rt
Immunogen Descrecombinant protein
ConjugateUnconjugated
Other NamesAlteplase antibody DKFZp686I03148 antibody Plasminogen activator tissue antibody Plasminogen activator tissue type antibody PLAT antibody Reteplase antibody t PA antibody T Plasminogen Activator antibody t-PA antibody T-plasminogen activator antibody Tissue plasminogen activator (t PA) antibody Tissue type plasminogen activator antibody Tissue-type plasminogen activator chain B antibody tPA antibody TPA_HUMAN antibody TPA1 antibody
Accession NoSwiss-Prot#:P00750
Uniprot
P00750
Gene ID
5327;
Calculated MW63 kDa
Formulation1*TBS (pH7.4), 1%BSA, 40%Glycerol. Preservative: 0.05% Sodium Azide.
StorageStore at -20˚C
Application Details
WB: 1:500-1:1000
IHC: 1:50-1:200
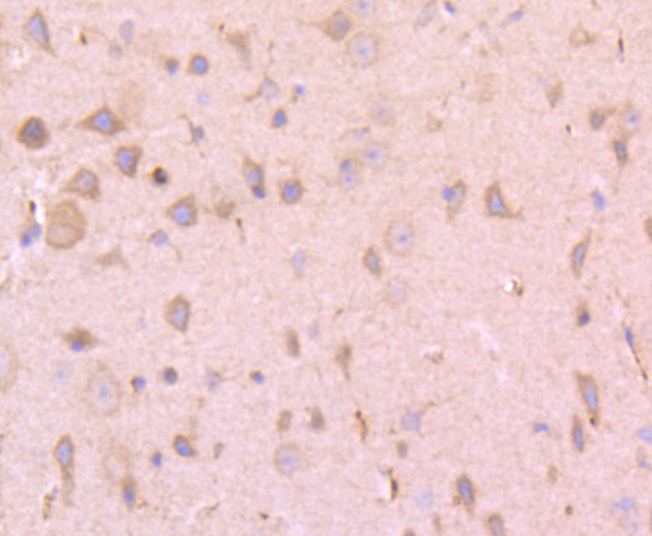
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded rat brain tissue using anti-PLAT antibody. Counter stained with hematoxylin.
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded mouse brain tissue using anti-PLAT antibody. Counter stained with hematoxylin.
uPA (urokinase-type plasminogen activator) and tPA (tissue plasminogen activator), which are serine proteases and members of the trypsin family, are essential to the intrinsic coagulation system. tPA is primarily involved in fibrinolysis, whereas uPA principally mediates cell migration and tissue remodeling processes. uPA and tPA are responsible for cleaving plasminogen, a large serum β-globulin that is deposited on the Fibrin strands within a thrombus. uPA and tPA preferentially target plasminogen at the Arg-Val bond to produce plasmin (also designated fibrinolysin), which is a trypsin-like enzyme that acts on Arg-Lys bonds in Fibrin and Fibrinogen and contributes to the systematic activation of the coagulation cascade. uPA and tPA each consist of two chains that are designated A and B. The A chain of uPA can be cleaved, resulting in low and high molecular mass forms. uPA and tPA are regulated by the serpin family members PAI-1 and PAI-2, which are serine proteinase inhibitors that complex with uPA, tPA and other targeted proteinases and then slowly disassociate to produce cleaved species that fold into stable inactive conformations.
If you have published an article using product 49333, please notify us so that we can cite your literature.



 Yes
Yes