Product Detail
Product NameNMDAR2A Rabbit mAb
Clone No.JA31-20
Host SpeciesRecombinant Rabbit
Clonality Monoclonal
PurificationProA affinity purified
ApplicationsWB, IHC
Species ReactivityHu, Ms, Rt
Immunogen Descrecombinant protein
ConjugateUnconjugated
Other NamesEPND antibody
FESD antibody
GluN2A antibody
Glutamate [NMDA] receptor subunit epsilon-1 antibody
Glutamate receptor antibody
Glutamate receptor ionotropic N methyl D aspartate 2A antibody
GRIN 2A antibody
GRIN2A antibody
hNR2A antibody
LKS antibody
N methyl D aspartate receptor channel, subunit epsilon 1 antibody
N Methyl D Aspartate Receptor Subtype 2A antibody
N methyl D aspartate receptor subunit 2A antibody
N-methyl D-aspartate receptor subtype 2A antibody
NMDA receptor subtype 2A antibody
NMDAR 2A antibody
NMDAR2A antibody
NMDE1_HUMAN antibody
NR2A antibody
OTTHUMP00000160135 antibody
OTTHUMP00000174531 antibody
Accession NoSwiss-Prot#:Q12879
Uniprot
Q12879
Gene ID
2903;
Calculated MW165 kDa
Formulation1*TBS (pH7.4), 1%BSA, 40%Glycerol. Preservative: 0.05% Sodium Azide.
StorageStore at -20˚C
Application Details
WB: 1:500
IHC: 1:50-1:100
Western blot analysis of NMDAR2A on rat brain tissue lysate using anti-NMDAR2A antibody at 1/1,000 dilution.
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded rat brain tissue using anti-NMDAR2A antibody. Counter stained with hematoxylin.
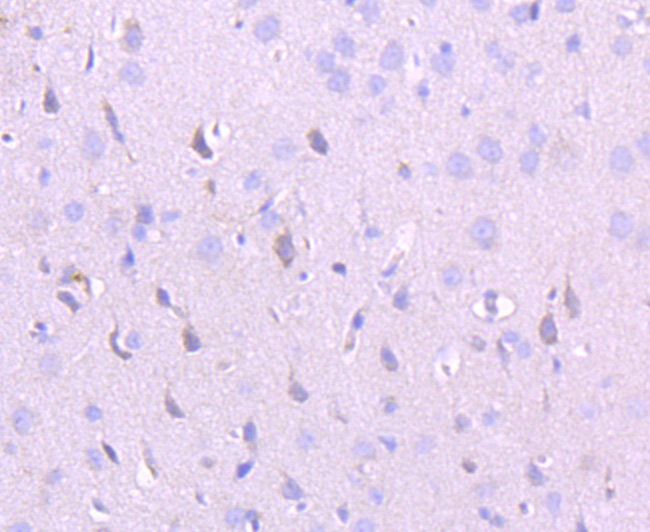
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded rat skin tissue using anti-NMDAR2A antibody. Counter stained with hematoxylin.
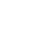
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human brain tissue using anti-NMDAR2A antibody. Counter stained with hematoxylin.
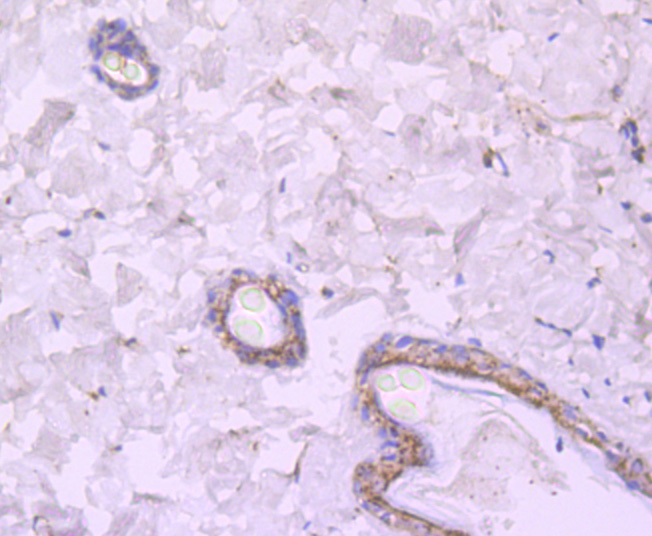
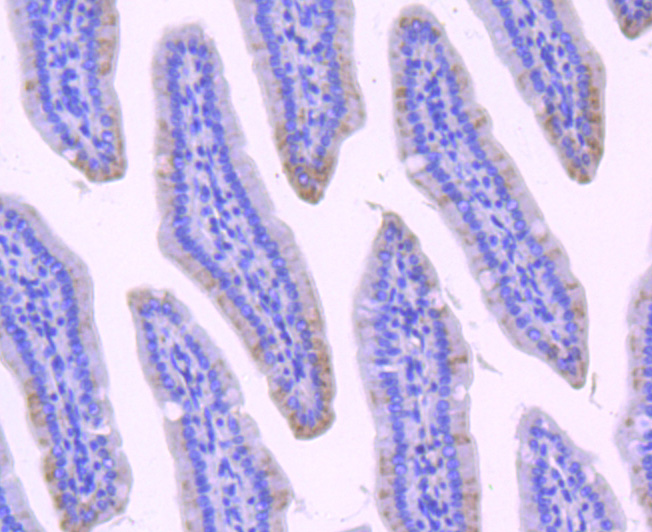
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded mouse small intestine tissue using anti-NMDAR2A antibody. Counter stained with hematoxylin.
NMDAR2A is a member of the glutamate-gated ion channel protein family. The encoded protein is an N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor subunit. NMDA receptors are both ligand-gated and voltage-dependent, and are involved in long-term potentiation, an activity-dependent increase in the efficiency of synaptic transmission thought to underlie certain kinds of memory and learning.
If you have published an article using product 49584, please notify us so that we can cite your literature.




 Yes
Yes