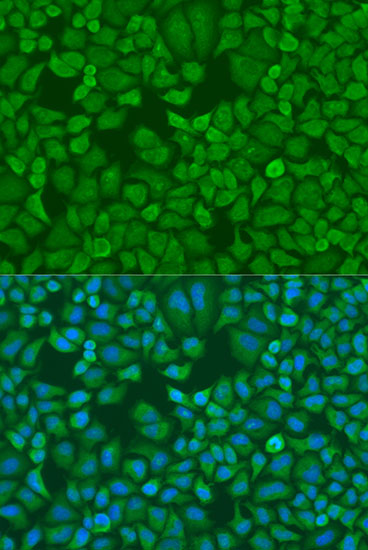
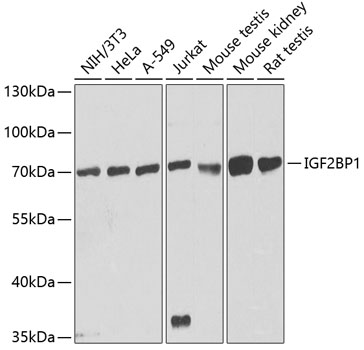
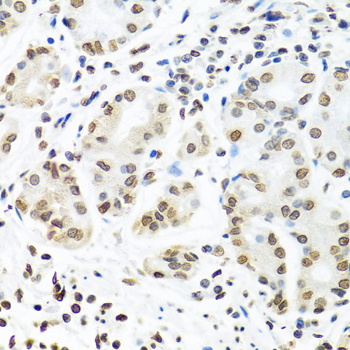
Insulin-like growth factor-II mRNA-binding proteins (IMPs) belong to a family of zipcode-binding proteins (1,2). Three members of this family, IMP1, IMP2, and IMP3, have been identified (1,2). They contain two RNA recognition motifs, four K homology domains, and were found to function in mRNA localization, turnover, and translation control (1,2). Research studies have implicated these proteins in a variety of physiological and pathological processes, such as growth and development (3), testicular neoplasia (4), and melanocytic neoplasia (5).